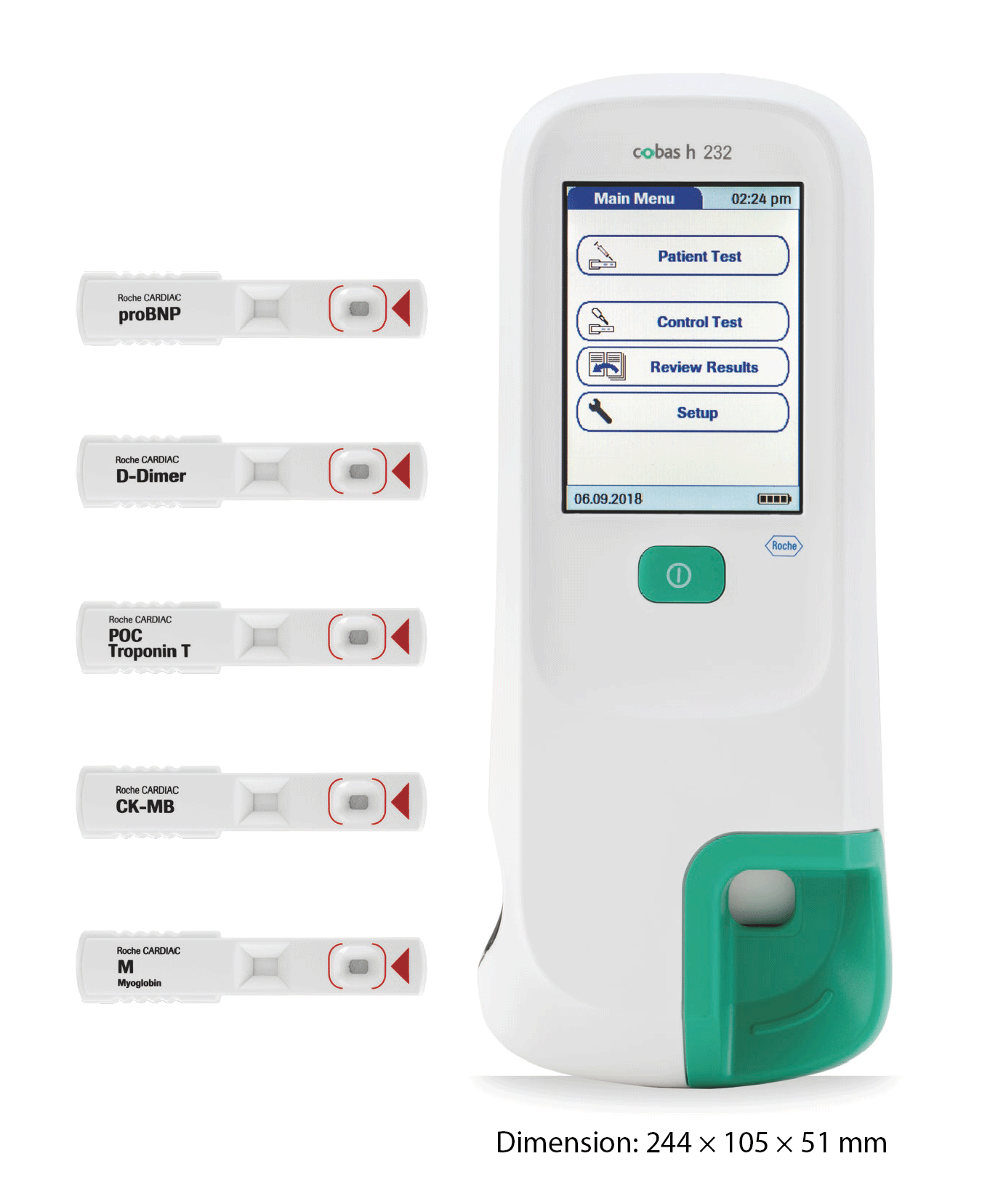
cobas h 232 – POC System


The cobas h 232 system enables confident on-the-spot diagnosis and management of patients presenting with signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease
Test multiple biomarkers
Confidently test for markers and make a differential diagnosis1-5.
- NT-proBNP Exclude heart failure (HF) and identify patients in need of further cardiac investigation2,7
- D-Dimer Rule out pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT)1,6
- Cardiac Troponin T Early rule in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and help identify patients with elevated mortality risk3,8,9
- CK-MB Aid in the diagnosis of AMI and detection of reinfarction4,8
- Myoglobin Support in the early diagnosis of AMI5,10
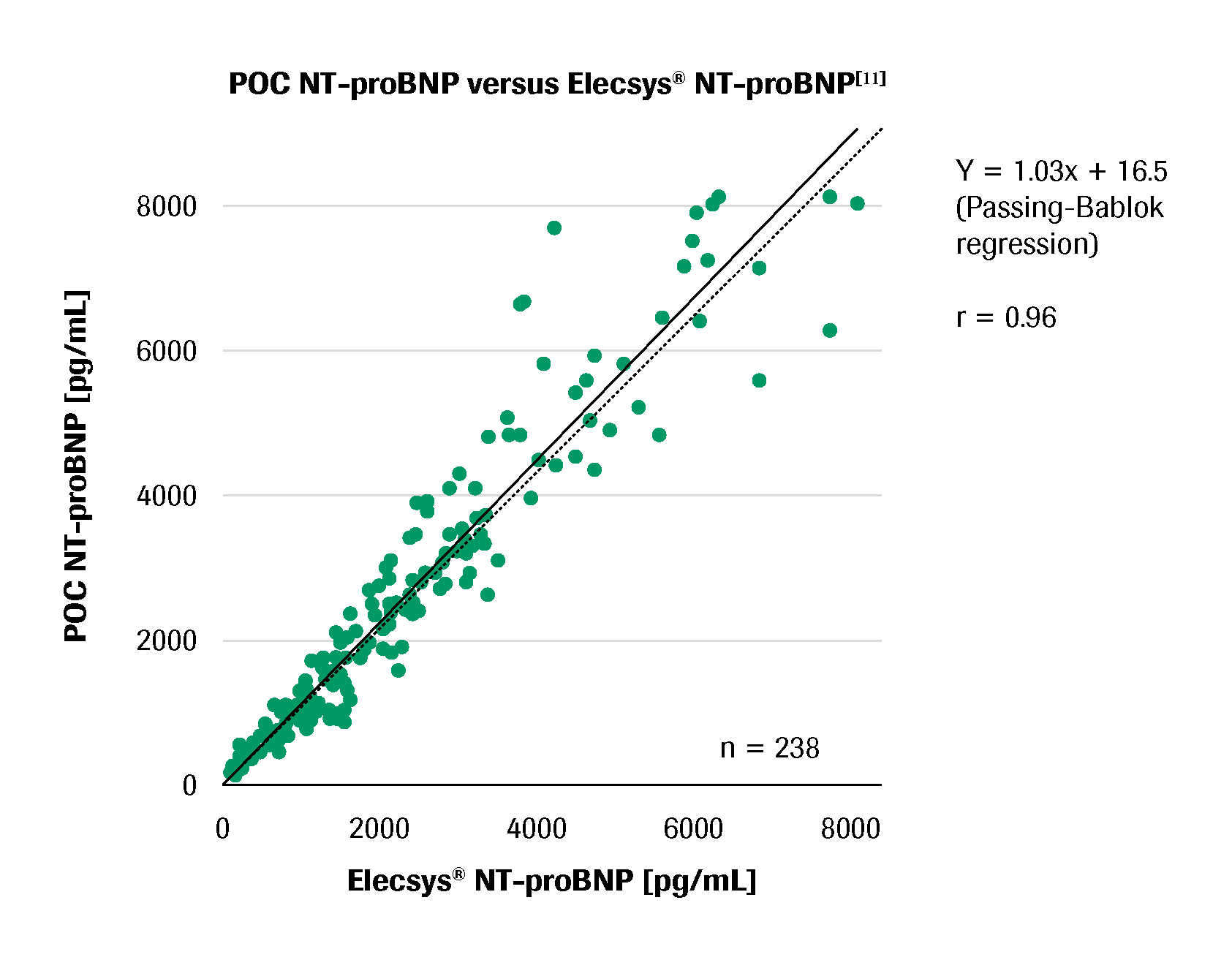
Accurate result
Result standardized with Roche central laboratory cobas® immunochemistry platforms11
cobas h 232 POC system
1 heparinised tube
Immunochemistry platforms
Fast-to-result
Result obtained in 8-12 minutes12
(Time varies with the assay used)
Easy to use
Small portable design
- No maintenance
- No calibration
- No sample preparation
How to Use
Ready to use
- No sample preparation12
- No calibration (automatic)12
- No warm up12
Test in 3 steps

1.Insert a Test Strip

2. Apply Sample
of 150ul heparinised whole blood using the Roche cardiac pipette
3. Read Results
3 Items needed for running a test:
1. Test strip (e.g NTproBNP)
2. Heparinized whole blood (sample)
3. 150ul pipette (to apply sample)
Ordering Package
| Material Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 04901142190 | cobas h232 instrument with scanner |
| 05533643190 | proBNP test strips (10 tests/box) |
| 04880668190 | Roche CARDIAC IQC |
| 11622889190 | Roche CARDIAC Pipettes, 20 disposable syringes (150 μL) |
Roche Diagnostics (Hong Kong) Limited
| Address: | Level 17, Metroplaza, Tower 1,223 Hing Fong Road, Kwai Chung, Hong Kong |
Phone: |
+852 2481 3387 |
| Fax: | +852 2418 0728 |
| [email protected] |
References:
- Roche CARDIAC D-Dimer-Method Sheet-package insert.
- Roche CARDIAC proBNP-Method Sheet-package insert.
- Roche CARDIAC POC Troponin T-Method Sheet-package insert.
- Roche CARDIAC CK-MB-Method Sheet-package insert.
- Roche CARDIAC M-Method Sheet-package insert.
- Konstantinides, S. et al. (2014). Eur Heart J 35, 3033-3080.
- Ponikowski, P. et al. (2016). Eur J Heart Fail 18(8), 891-975.
- Roffi , M. et al. (2015). Eur Heart J 37(3), 267-315.
- Stengaard, C. et al. (2013). American J Cardiol 112(9), 1361-1366.
- Achar, S.A. et al. (2005). Am Fam Physician 72(1), 119-126.
- Bertsch, T. et al. (2010). Clin Lab. 56(1-2), 37-49. ; Jungbauer, C. et al. (2017). Cli Lab 63(4), 633-645.
- Roche (2016). cobas h 232 POC system Operator’s Manual, Version 6.0.
DS-2023-JUL-001
What is NT-proBNP?

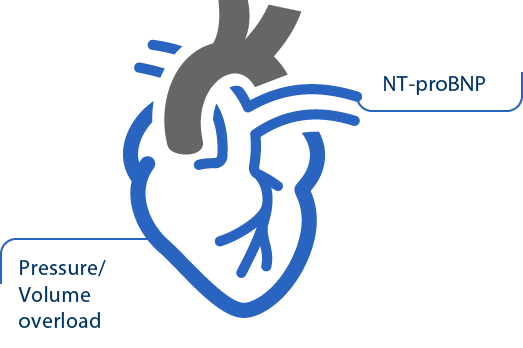
Natriuretic peptides, including NT-proBNP, are produced within cardiomyocytes in response to stress, and are released after clinical triggers.12
Use as an initial diagnostic test
In association with clinical evaluation,* NT-proBNP can support decision-making in HF diagnosis in acute and non-acute Settings.
- Exclude HF and avoid unnecessary echocardiography6-8
- Identify patients with high probability of having HF and need further investigation2
- In primary care, identify patients who need referral to the specialist6-8
Interpretation of NT-proBNP results in patients presenting
in non-acute setting1-5
Roche NT-proBNP
<125pg/mL HF unlikely,
consider other diagnoses
Roche NT-proBNP
Roche NT-proBNP
>125pg/mL
HF likely,
perform
echocardiography to
confirm the diagnosis
of HF
Interpretation of NT-proBNP results in patients presenting
in non-acute setting9-13
Roche NT-proBNP

Roche NT-proBNP
<125pg/mL HF unlikely,
consider other diagnoses
Roche NT-proBNP
>125pg/mL
HF likely,
perform
echocardiography to
confirm the diagnosis
of HF
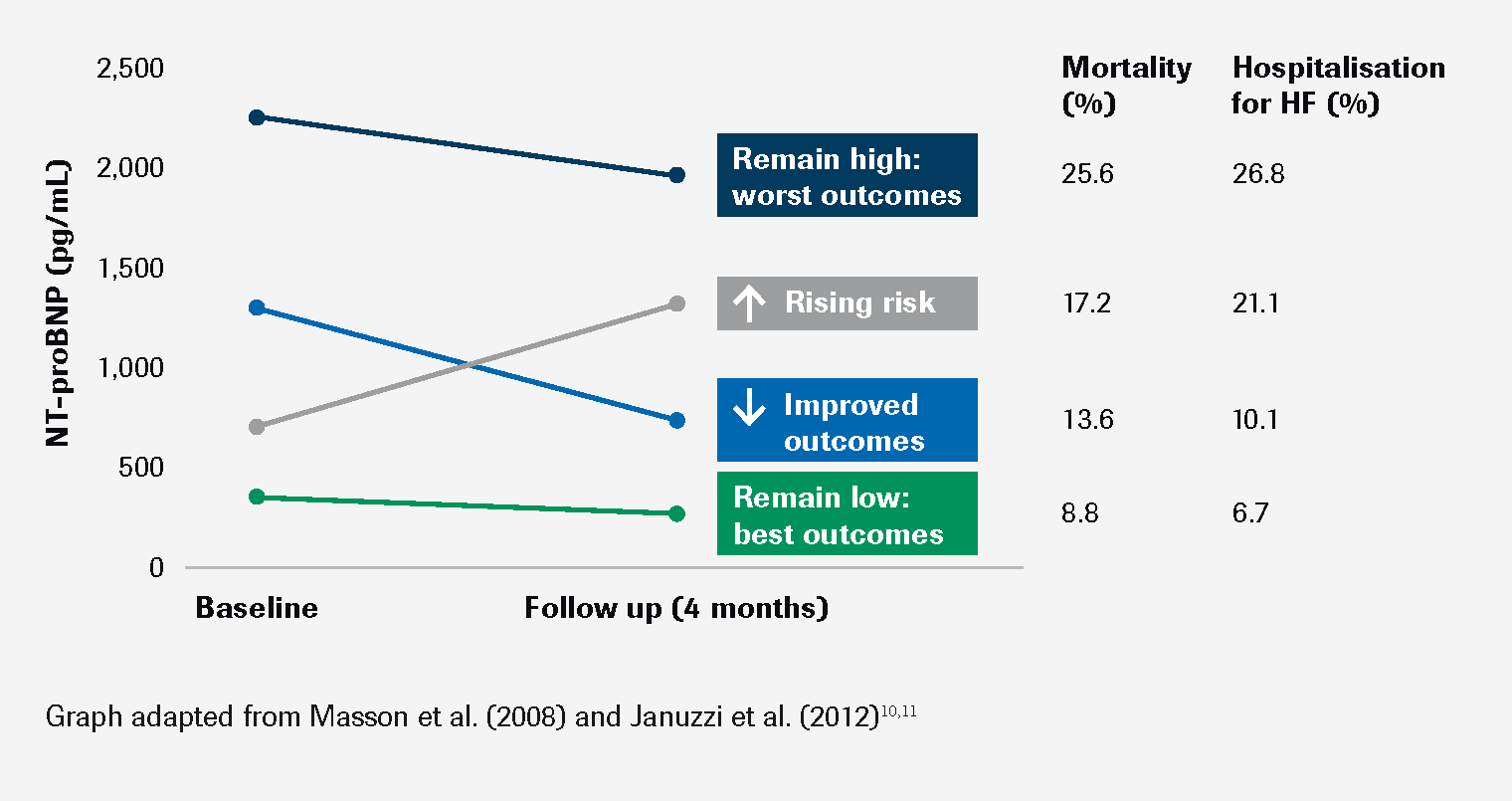
Use as out patient monitoring
NT-proBNP can be used to monitor disease progression or patient improvement in out-patient setting
Monitoring NT-proBNP levels helps to manage HF well over the long term, regardless of symptoms or medication being taken, in particular angiotensin receptor-neprilysininhibitors (ARNis)9.
ⓘKnow more about NT-proBNP
References:
- Rutten et al. https://ipccs.org/2017/12/10/epccs-practical-guidance-on-heart-failurediagnosis-and-management-in-primary-care/ (Accessed May 24 2022).
- Ponikowski P, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18(8):891-975. doi:10.1002/ejhf.592.
- Taylor CJ, et al. Primary care REFerral for EchocaRdiogram (REFER) in heart failure: a diagnostic accuracy study. Br J Gen Pract. 2017;67(655):e94-e102. doi:10.3399/bjgp16X688393.
- Taylor et al. (2017). Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation, No. 4.3. National Institute for Health Research. ISSN 2050-4365.
- Hildebrandt P, Collinson PO, Doughty RN, et al. Age-dependent values of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide are superior to a single cut-point for ruling out suspected systolic dysfunction in primary care. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(15):1881-1889. oi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq163.
- Taylor, C.J. et al. (2017). Br J Gen Pract. 67(655), e94-e102.
- Taylor, C.J. et al. (2017). Effi cacy and Mechanism Evaluation, No. 4.3. National Institute for Health. Research. ISSN 2050-4365. [Accessed September 2018].
- British Heart Foundation and the All-Party Parliamentary Group on Heart Disease (2016). Focus on Heart Failure. Report accessible on https://www.bhf.org.uk/get-involved/campaigning/inquiry-intoliving-with-heart-failure [Accessed September 2018].
- Januzzi, J.L. et al. (2016). Clin Chem 62(5), 663-665.
- Masson, S. et al. (2008). J Am Coll Cardiol 52, 997-1000.
- Januzzi (2012). Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 105(1), 40-50
- Weber M, Hamm C. Role of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and NT-proBNP in clinical routine. Heart. 2006;92(6):843-849. doi:10.1136/hrt.2005.071233.
- McKie PM, Burnett JC Jr. NT-proBNP: The Gold Standard Biomarker in Heart Failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(22):2437-2439. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.001.
- Huelsmann M, et al. NT-proBNP has a high negative predictive value to rule-out short-term cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(18):2259-2264. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn334.
- Huelsmann M, et al. PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(15):1365-1372. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069.
- Scirica BM, et al. Heart failure, saxagliptin, and diabetes mellitus: observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 randomized trial [published correction appears in Circulation. 2015 Oct 13;132(15):e198]. Circulation. 2014;130(18):1579-1588. doi:10.1161/ CIRCULATIONAHA.114.010389.
- Einarson TR, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007-2017. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):83. Published 2018 Jun 8. doi:10.1186/s12933-018-0728-6.
DS-2023-JUL-001

