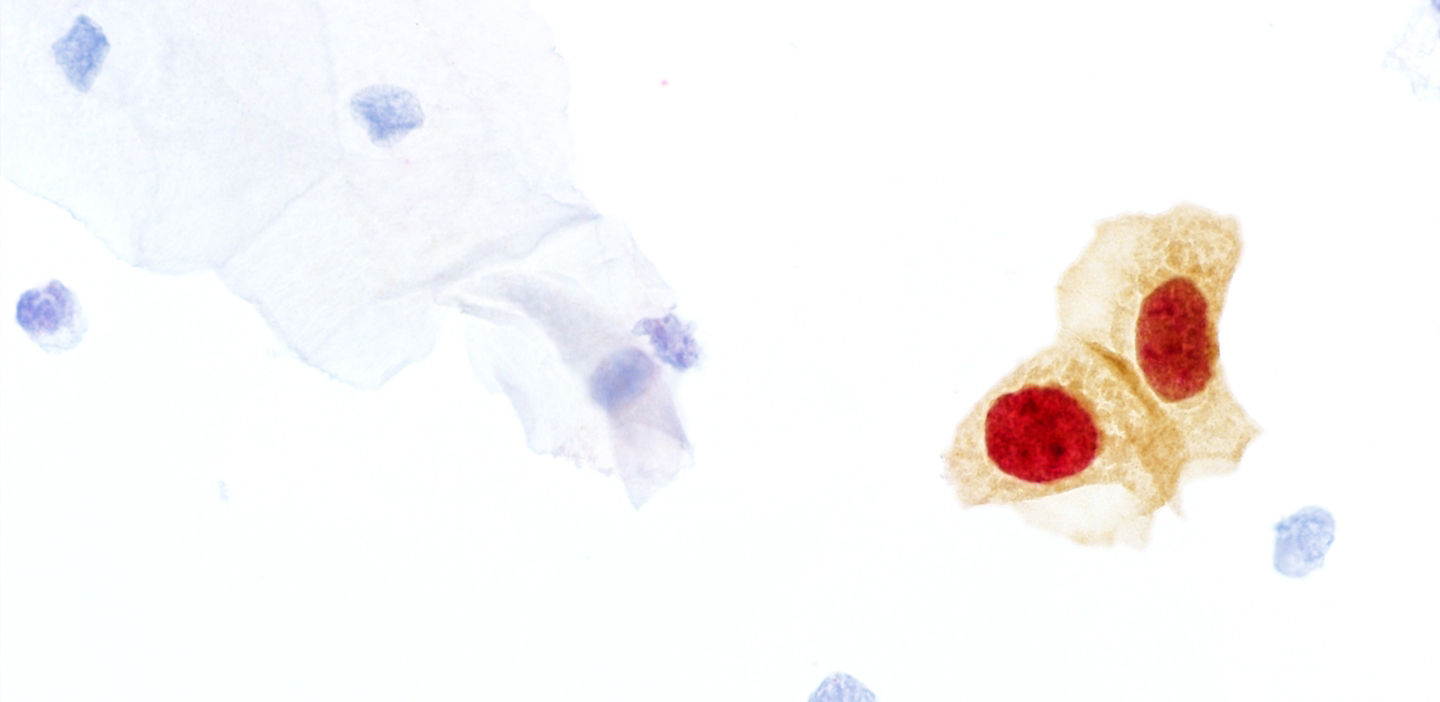
Test CINtec® PLUS Cytology

Le test CINtec® PLUS Cytology est un test de double-immunomarquage validé cliniquement qui détecte les biomarqueurs antagonistes p16 et Ki-67 dans les prélèvements cytologiques cervico-utérins1 .
L'expression simultanée de p16 et Ki-67 dans la même cellule est fortement associée à un stade précancéreux de haut grade du cancer du col de l'utérus2,3.
CINtec® PLUS Cytology
Le rationnel d’un double marquage

La protéine p16INK4a joue un rôle majeur antiprolifératif durant la progression du cycle de division cellulaire (marquage brun).
Ki-67 est une protéine associée à la prolifération qui peut être détectée exclusivement dans le noyau des cellules en prolifération (marquage rouge).
L’expression conjointe de ces deux marqueurs est le signe d’une dérégulation cellulaire.
CINtec® PLUS Cytology
Sa place dans les recommandations françaises4
Le test CINtec® PLUS Cytology constitue une aide au triage pour le dépistage du cancer du col de l’utérus
Le double immunomarquage p16/Ki67 est recommandé en option pour le triage des cytologies ASC-US et LSIL des femmes de moins de 30 ans (ou de 25 à 30 ans).

* Primary, ASC-US, LSIL Marker Study : étude prospective, multicentrique, internationale, menée chez plus de 27 000 femmes dont 304 cas LSIL.
Pour les femmes de moins de 30 ans présentant une cytologie LSIL, on observe une réduction du nombre de colposcopie d’environ 45 % en utilisant CINtec® PLUS versus l’absence de triage.
CINtec® PLUS Cytology
Une solution adaptée à vos besoins
Nos Kits sont disponibles en version manuelle ou entièrement automatisée sur les instruments de la gamme VENTANA BenchMark1,5

CINtec® PLUS Cytology
Pour en apprendre davantage
Les publications suivantes contiennent des données probantes supplémentaires des avantages cliniques du double marquage p16/Ki-67 lors du dépistage du cancer du col de l’utérus :
- Schmidt D, Bergeron C, Denton KJ, Ridder R for the European CINtec Cytology Study Group. p16/Ki-67 dual-stain cytology in the triage of ASCUS and LSIL papanicolaou cytology: results from the European equivocal or mildly abnormal Papanicolaou cytology study. Cancer Cytopathol. 2011;119(3):158-166. doi: 10.1002/cncy.20140. Epub 2011 Mar 25.
- Petry KU, Schmidt D, Scherbring S, et al. Triaging Pap cytology negative, HPV positive cervical cancer screening results with p16/Ki-67 dual-stained cytology. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;121(3);505-509. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.02.033. Epub 2011 Mar 21.
- Killeen JL, Dye T, Grace C, Hiraoka M. Improved abnormal Pap smear triage using cervical cancer biomarkers. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2014;18(1):1-7. DOI:10.1097/LGT.0b013e31828aeb39.
- Ikenberg, H. et al., Screening for Cervical Cancer Precursors With p16/Ki-67 Dual-Stained Cytology: Results of the PALMS Study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Oct 16; 105(20): 1550-1557.
- KU Petry et al., A model to evaluate the costs and clinical effectiveness of human papilloma virus screening compared with annual papanicolaou cytology in Germany. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 212 (2017) 132–139.
- T.C. Wright Jr. et al., Triaging HPV-Positive Women with p16/Ki-67 Dual-stained Cytology: Results from a Sub-study Nested into the ATHENA Trial. Gynecologic Oncology 144 (2017) 51–56.Gynecol Oncol. 2017 Jan;144(1):51-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.10.031.
- Bergeron, C. et al., Prospective evaluation of p16/Ki-67 dual-stained cytology for managing women with abnormalPapanicolaou cytology: PALMS study results. Cancer Cytopathol. 2015 Jun;123(6):373-81. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21542. Epub 2015 Apr 17.
- Wentzensen N., et al., Performance of p16/Ki-67 Immunostaining to Detect Cervical Cancer Precursors in a Colposcopy Referral Population. Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 1;18(15):4154-62. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0270. Epub 2012 Jun 6.
- Wentzensen N., et al., p16/Ki-67 Dual Stain Cytology for Detection of Cervical Precancer in HPV-Positive Women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Sep 15;107(12):djv257. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv257. Print 2015 Dec.
- Waldstrøm, M., et al., Evaluation of p16INK4a/Ki-67 Dual Stain in Comparison With an mRNA Human Papillomavirus Test on Liquid-Based Cytology Samples With Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion. Cancer Cytopathol. 2013 Mar;121(3):136-45. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21233. Epub 2012 Sep 17.
Références :
- Fiche technique CINtec® PLUS, revision D, 02/2016
- Bergeron C, Ikenberg H, Sideri M, Denton K, Bogers J, Schmidt D et al. Prospective evaluation of p16/Ki-67 dual-stained cytology for managing women with abnormal Papanicolaou cytology: PALMS study results. Cancer Cytopathol2015;123(6):373-81.
- Schmidt D, Bergeron C, Denton KJ, Ridder R, European CINtec Cytology Study Group. p16/ki-67 dual-stain cytology in the triage of ASCUS colposcopy triage: data from the randomized Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance/Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Triage Study (ALTS). J Natl Cancer Inst 2002;94(2):102-7.
- INCa, Conduite à tenir devant une femme ayant une cytologie cervico-utérine anormale - Thésaurus, Collection recommandations et référentiels/recommandations pratiques clinique. 2016
- Fiche technique CINtec® PLUS Kit, révision 2.3, 2009
Le CINtec® PLUS Cytology Kit est un test d'immunocytochimie qui permet la détection qualitative simultanée des protéines p16INK4a et Ki-67 dans les préparations cytologiques cervicales. L'interprétation des résultats du test doit être réalisée par un professionnel certifié en tenant compte des antécédents cliniques de la patiente et des tests diagnostiques supplémentaires effectués. Ce produit est conçu pour être utilisé en diagnostic in vitro (DIV)"
Dispositif médical de diagnostic in vitro.
Fabricant : Roche Diagnostics GmbH (Allemagne) – Distributeur : Roche Diagnostics France
Lire attentivement les instructions figurant dans la fiche technique
MC-FR-00849